Pendampingan Bubble Wrap Exercise Therapy Pada Pasien dengan Distress Diabetes di Wahana Cipta Sinatria Karanganyar
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.61231/jp2m.v1i4.142Keywords:
Bubble Wrap Therapy, Distress Diabetes, Diabetes MellitusAbstract
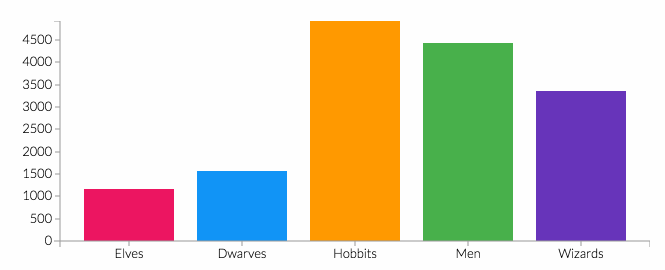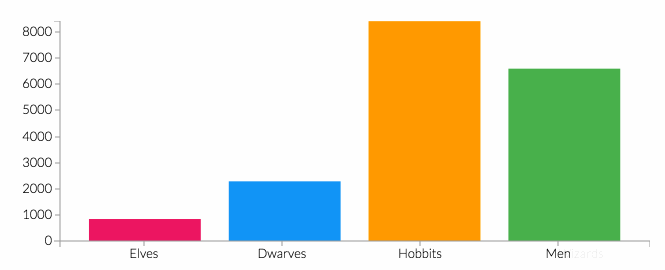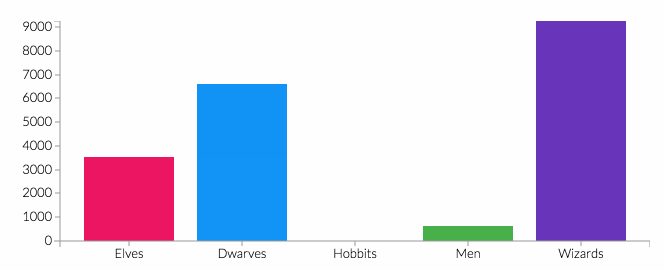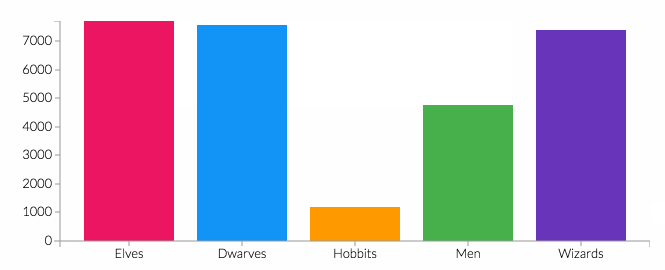
The prevalence of psychological comorbidities in people with diabetes worldwide is nearly a quarter of people suffer from symptoms of depression or diabetes distress. Management to reduce a person's stress level based on several studies entitled Popping Sealed Air Capsules to Reduce Stress by Dillon KM. The purpose of this service is according to the Bubble Wrap Therapy Training is expected to reduce stress in patients with DM. The method used is a demonstration of bubble wrap exercise training for 15 minutes each part of the feet and hands by pressing bubble wrap using feet and hands and providing health education for 30 minutes on the importance of controlling stress levels in patients with DM. The results of the service show the level of stress with the results of BWET AD ACL from moderate stress level 68.75%, to mild 56.25%. Conclusion Bubble wrap therapy training effectively reduces the level of diabetic distress at Wahana Cipta Sinatria Karanganyar.References
Dewi, C. F., Demang, F. Y., Suryati, Y., Djerubu, D., & Banul, M. S. (2023). Hubungan antara Psychological Distress dengan Hipertensi pada Masyarakat di Kabupaten Manggarai. Malahayati Nursing Journal, 5(1), 277–289. https://doi.org/10.33024/mnj.v5i1.7129
Dillon, K. M., Minchoff, B., & Baker, K. H. (1985). Positive emotional states and enhancement of the immune system. International Journal of Psychiatry in Medicine, 15(1), 13–18. https://doi.org/10.2190/r7fd-urn9-pq7f-a6j7
Erener, S. (2020). Diabetes, infection risk and COVID-19. Molecular Metabolism, 39, 101044. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molmet.2020.101044
Fiorillo, A., & Gorwood, P. (2020). The consequences of the COVID-19 pandemic on mental health and implications for clinical practice. European Psychiatry, 63(1). https://doi.org/10.1192/j.eurpsy.2020.35
Gunawan, S., & Rahmawati, R. (2021). Hubungan Usia, Jenis Kelamin dan Hipertensi dengan Kejadian Diabetes Mellitus Tipe 2 di Puskesmas Tugu Kecamatan Cimanggis Kota Depok Tahun 2019. ARKESMAS (Arsip Kesehatan Masyarakat), 6(1), 15–22. https://doi.org/10.22236/arkesmas.v6i1.5829
Halepian, L., Saleh, M. B., Hallit, S., & Khabbaz, L. R. (2018). Adherence to Insulin, Emotional Distress, and Trust in Physician Among Patients with Diabetes: A Cross-Sectional Study. Diabetes Therapy, 9(2), 713–726. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13300-018-0389-1
Infodatin, 2020. (n.d.).
Kane, N. S., Hoogendoorn, C. J., Tanenbaum, M. L., & Gonzalez, J. S. (2018). Physical symptom complaints, cognitive emotion regulation strategies, self-compassion and diabetes distress among adults with Type 2 diabetes. Diabetic Medicine, 35(12), 1671–1677. https://doi.org/10.1111/dme.13830
Khasanah, D. U., Himawan, F., & Suparjo, S. (2021). Stress Levels for People With Diabetes Mellitus During the Covid-19 Pandemic. Juru Rawat. Jurnal Update Keperawatan, 1(1), 39–43. https://doi.org/10.31983/juk.v1i1.8065
Listrikawati, M., & Batubara, I. M. (2018). Gerakan Latensi Giras Sebagai Upaya Preventif. Jurnal Pengabdian Kepada Masyarakat: Kesehatan, 2, 41–49.
Minuljo, T. T., Anindita, Y. P. C., Seno, H. N. H., Pemayun, T. G. D., & Sofro, M. A. U. (2020). Karakteristik dan Keluaran Pasien COVID-19 dengan DM di RS Umum Pusat Dr. Kariadi (Tinjauan pasien periode Maret-Juli 2020). Medica Hospitalia?: Journal of Clinical Medicine, 7(1A), 150–158. https://doi.org/10.36408/mhjcm.v7i1a.473
Nursucita, A., & Handayani, L. (2021). Factors Causing Stress in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients. Jambura Journal of Health Sciences and Research, 3(2), 304–313. https://doi.org/10.35971/jjhsr.v3i2.10505
Putra, A. R. ., Dewi, I. N. ., Triana, L. ., & Afriani, R. I. . (2023). Pemberdayaan Masyarakat Kecamatan Pulomerak dalam Penurunan Stunting Melalui Posyandu Keliling . Jurnal Penelitian Dan Pengabdian Masyarakat, 1(2), 57–69. https://doi.org/10.61231/jp2m.v1i2.73
Setiyorini, E., Wulandari, N. A., & Efyuwinta, A. (2018). Hubungan kadar gula darah dengan tekanan darah pada lansia penderita Diabetes Tipe 2. Jurnal Ners Dan Kebidanan (Journal of Ners and Midwifery), 5(2), 163–171. https://doi.org/10.26699/jnk.v5i2.art.p163-171
Siregar, R. (2022). Diabetes Mellitus Tipe 2 dan Akses Pelayanan Kesehatan: Pengalaman Selama Covid-19. In UMSU Pres.
Soelistijo, S. (2021). Pedoman Pengelolaan dan Pencegahan Diabetes Melitus Tipe 2 Dewasa di Indonesia 2021. Global Initiative for Asthma, 46. www.ginasthma.org.
Tanto, C., Liwang, F., Hanifati, S., & Pradipta, E. A. (2014). kapita selekta . edisi IV.
Webber, S. (2021). International Diabetes Federation, 2021. In Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice (Vol. 102, Issue 2). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diabres.2013.10.013
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Martini Listrikawati, Mellia Silvy Irdianty, Deoni Vioneery, Noor Fitriyani

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
You are free to:
- Share — copy and redistribute the material in any medium or format for any purpose, even commercially.
- Adapt — remix, transform, and build upon the material for any purpose, even commercially.
- The licensor cannot revoke these freedoms as long as you follow the license terms.
Under the following terms:
- Attribution — You must give appropriate credit , provide a link to the license, and indicate if changes were made . You may do so in any reasonable manner, but not in any way that suggests the licensor endorses you or your use.
- No additional restrictions — You may not apply legal terms or technological measures that legally restrict others from doing anything the license permits.
Notices:
You do not have to comply with the license for elements of the material in the public domain or where your use is permitted by an applicable exception or limitation .
No warranties are given. The license may not give you all of the permissions necessary for your intended use. For example, other rights such as publicity, privacy, or moral rights may limit how you use the material.