Cek Gula, Cek BMI, Cegah Diabetes: Implementasi Program Pengabdian Masyarakat dalam Pencegahan Penyakit Tidak Menular
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.61231/s4hw2n86Keywords:
Diabetes, Glukosa, Indeks Massa Tubuh, Penyakit Tidak MenularAbstract
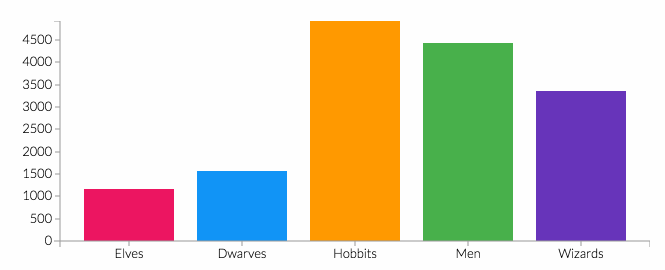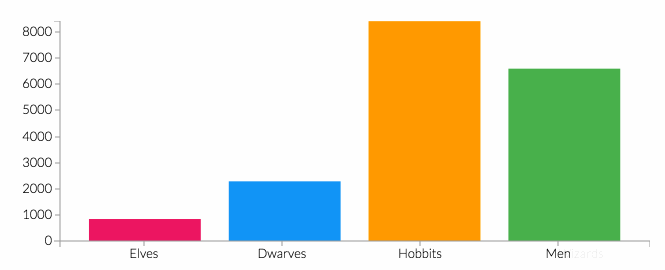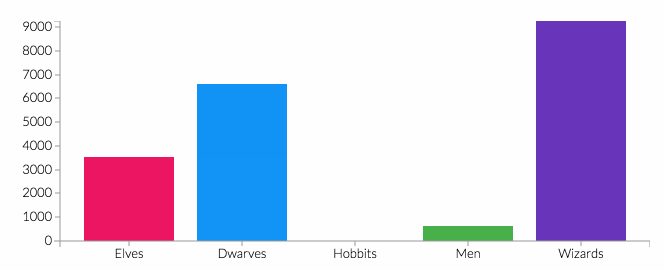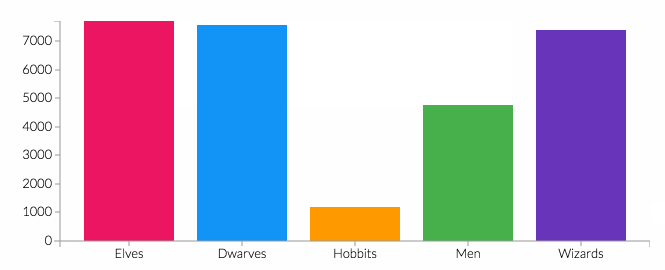
This community service activity aims to increase public awareness and the ability to detect diabetes risk early through blood glucose level checks, Body Mass Index (BMI) measurements, health education, and mentoring healthy behavior changes. The approach used included initial assessments, building communication with residents, forming support groups, implementing education, and program evaluation. A total of 30 participants participated in the screening activity. The results showed that 66.67% were in the age group ≤55 years and 80.00% were female. Based on nutritional status, 43.33% of participants were obese and 26.67% were overweight. Blood pressure checks showed 36.67% had hypertension, while 40.00% had high blood glucose levels. These findings illustrate the high prevalence of modifiable risk factors in the community. The implementation of education was proven to increase participants' understanding of diet management, physical activity, and the importance of routine screening, as demonstrated by active involvement and positive responses from participants.
References
Abdullah, A., Mahmud, S., & Rahman, F. (2022). Community-based intervention for metabolic disease prevention: A systematic review. BMC Public Health, 22(1), 1152.
Afshin, A., Forouzanfar, M. H., & Reitsma, M. (2017). Health effects of overweight and obesity in 195 countries. The New England Journal of Medicine, 377(1), 13–27.
Cho, N. H., Shaw, J. E., & Karuranga, S. (2022). Global epidemiology of diabetes and projections for 2030. Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice, 185, 109289.
Heymsfield, S. B., & Wadden, T. A. (2017). Mechanisms, pathophysiology, and management of obesity. The New England Journal of Medicine, 376(3), 254–266.
International Diabetes Federation. (2021). IDF Diabetes Atlas (10th ed.).
Jafar, T. H., Haaland, B., & Islam, M. (2021). Effectiveness of lifestyle interventions in reducing metabolic risk in community settings. The Lancet Global Health, 9(6), e802–e812.
Kemenkes RI. (2022). Laporan Nasional Riskesdas 2022.
Khan, M. A., Hashim, M. J., & King, J. K. (2020). Epidemiology of diabetes. International Journal of Endocrinology, 2020, 1–12.
Mohamed, A. F., Yusuf, S., & Rahmawati, D. (2023). Health education strategies for metabolic disease prevention: Evidence from community programs. Journal of Community Health, 48(2), 450–458.
Putri, E. D., Santoso, B., & Yuliana, I. (2021). Awareness of routine glucose monitoring among Indonesian adults. Journal of Public Health Research, 10(3), 256–263.
Rizki, E., Ardiansyah, A., & Widodo, A. (2021). Association between lifestyle factors and obesity in Indonesian adults. Nutrients, 13(11), 4002.
Saeedi, P., Petersohn, I., & Salpea, P. (2020). Global and regional diabetes prevalence estimates for 2019 and projections for 2030. Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice, 157, 107843.
WHO. (2021). Noncommunicable diseases progress monitor 2021
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2026 Trisakti Halimah Delimasari , Annisa’ Arifatul Hikmah, Elsa Tursina , Riska Fajar Fathony, Muhammad Yusuf

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
You are free to:
- Share — copy and redistribute the material in any medium or format for any purpose, even commercially.
- Adapt — remix, transform, and build upon the material for any purpose, even commercially.
- The licensor cannot revoke these freedoms as long as you follow the license terms.
Under the following terms:
- Attribution — You must give appropriate credit , provide a link to the license, and indicate if changes were made . You may do so in any reasonable manner, but not in any way that suggests the licensor endorses you or your use.
- No additional restrictions — You may not apply legal terms or technological measures that legally restrict others from doing anything the license permits.
Notices:
You do not have to comply with the license for elements of the material in the public domain or where your use is permitted by an applicable exception or limitation .
No warranties are given. The license may not give you all of the permissions necessary for your intended use. For example, other rights such as publicity, privacy, or moral rights may limit how you use the material.